Buffer Definition Biology
It keeps the pH within the proper range. It is a water-based salt solution containing disodium hydrogen phosphate sodium chloride and in some formulations potassium chloride and potassium dihydrogen phosphate.
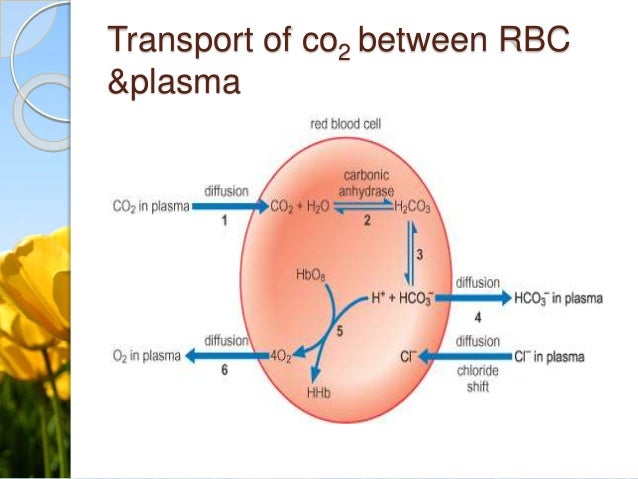
Carbon dioxide is part of a prominent buffer system in the human body.

Buffer definition biology. Buffer solution a solution containing such a compound. A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. Acids give up protons bases accept them.
An ionic compound usually a salt of a weak acid or base added to a solution to resist changes in its acidity or alkalinity and thus stabilize its pH. How to use buffer in a sentence. This buffer system involves carbonic acid H 2 CO 3 and bicarbonate HCO 3 anion.
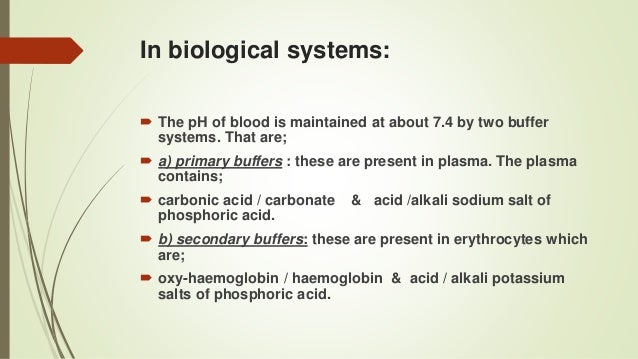
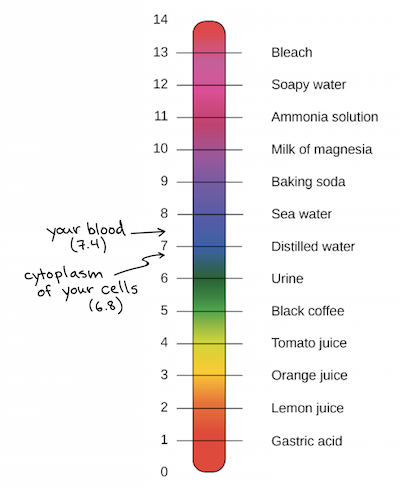
Buffer definition is - fellow man. Return to Search Page. The pH of blood is maintained 74 when the buffer ratio becomes 20.
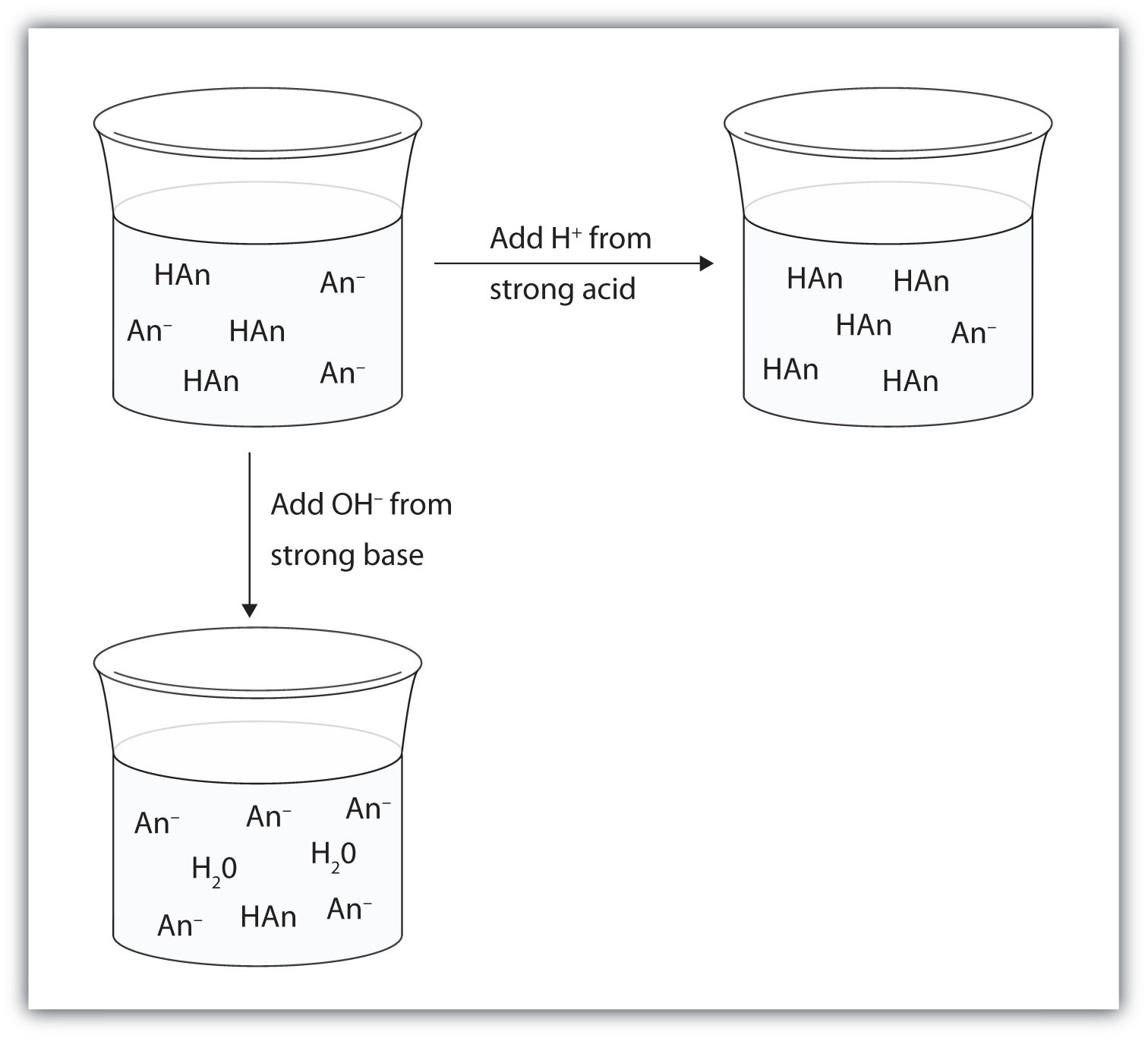
Buffer Definition - Chemistry and Biology DEFINITION A buffer is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid its salt or a weak base its salt that resist a change in pH on the addition of either acid or base. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. Write the chemical equation.
Buffer in chemistry solution usually containing an acid and a base or a salt that tends to maintain a constant hydrogen ion concentration. For instance one of the buffers that maintain the pH of human blood involves carbonic acid H. Make room between questions.
HA --- H A -. In nature there are many systems that use buffering for pH regulation. Most buffers consist of a weak acid and a weak base.
A buffer is an aqueous solution used to keep the pH of a solution nearly constant. Basically buffers are molecules that donate or accept protons to resist changes in pH as acids or bases are added to the solution. An example of a common buffer is a solution of acetic acid CH 3 COOH and sodium acetate.
1 chemistry A buffer solution. Parts A B in the prep notes water and pH 1 point Water Ionizes. 2 biochemistry An ionic compound that when added to a solution neutralizes both acids and bases without significantly changing the original acidity or alkalinity of a solution.
Relate this concept to pH. Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications. The buffer helps to maintain a constant pH.
The dissociation of a simple acid HA can be described by the following chemical reaction. Buffers typically consist of an acid-base pair with the acid and base differing by the presence or absence of a proton a conjugate acid-base pair. The bicarbonate buffer neutralizes stronger dietary and metabolic acids HA converting them into weak bases A with the increase in H 2 CO 3.
Phosphate-buffered saline abbreviated PBS is a buffer solution commonly used in biological research. Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained one or more electrons. Adilah Anwar Jaya Barad Jacquelyn Calhoun and Sammi Chadrow Note that each question has multiple parts that must be answered.
For the body to function properly it is essential that there is tight pH regulation which maintains the body generally at a neutral pH of 74. For example the bicarbonate buffering system is used to regulate the pH of blood. A solution containing either a weak acid and a conjugate base or a weak base and a conjugate acid used to stabilize the pH of a liquid upon dilution.
If too much H enters the body bicarbonate will combine with the H to create carbonic acid and limit the decrease in pH. OH 2 H 2 O H 3 O Kw is the. Buffer a chemical substance which has the capacity to bond to H ions removing them from solution when their concentration begins to rise and releasing H ions when their concentration begins to fall.
In water solution sodium acetate is completely dissociated into sodium Na and acetate CH 3 COO - ions. A biological buffer is an organic substance that has a neutralizing effect on hydrogen ions. Buffer capacity A measure of the ability of a solution to maintain its pH in the face of the addition of acid or alkali.
In this way buffers stabilize the pH of biological solutions and are thus important in maintaining HOMEOSTASIS. Buffer hydrogen ion buffer or buffer solution. Lab 4 Buffers and pH group assignment Names.
A person or thing that lessens shock or protects from damaging impact circumstances etc. A capacity of 1 when 1 mol of acid or alkali is added to 1 litre causes a pH fall or rise of 1 pH unit. Buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base that can be added before the pH of a buffer changes.
Stronger bases B are also changed into weak acids BH with the rise in HCO 3. A buffer solution is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa. A buffer consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
Buffers are aqueous solutions that resist changes in pH or the acidity or basicity of a solution relative to other substances. In this way a biological buffer helps maintain the body at the correct pH so that biochemical processes continue to run optimally. Buffers in a biological system keep the pH potential hydrogen constant when there are changes in the hydrogen H ion.
 Special Properties Of Water Help Biomolecules And The Chemistry Of Life Study Guide Shmoop
Special Properties Of Water Help Biomolecules And The Chemistry Of Life Study Guide Shmoop
 Buffer Buffering Capacity Properties Of Good Buffer And Role Of Buffer In Vitro And In Vivo Online Biology Notes
Buffer Buffering Capacity Properties Of Good Buffer And Role Of Buffer In Vitro And In Vivo Online Biology Notes
 Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Solutions Electron Configuration
Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Solutions Electron Configuration
 10 5 Buffers The Basics Of General Organic And Biological Chemistry
10 5 Buffers The Basics Of General Organic And Biological Chemistry
 Buffer Solutions Biochemistry The Biology Notes
Buffer Solutions Biochemistry The Biology Notes
 Water Acids And Bases Biology Library Science Khan Academy
Water Acids And Bases Biology Library Science Khan Academy
 Bromothymol Blue Definition Uses Formula Chemistry Class Video Study Com
Bromothymol Blue Definition Uses Formula Chemistry Class Video Study Com
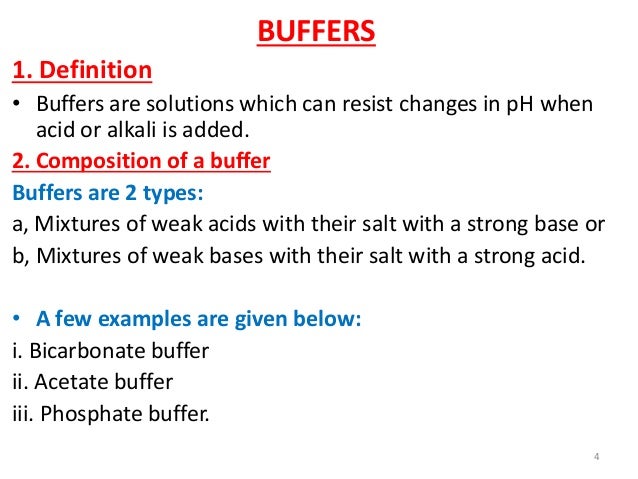 Lec 9 Level 4 De Biological Buffer
Lec 9 Level 4 De Biological Buffer
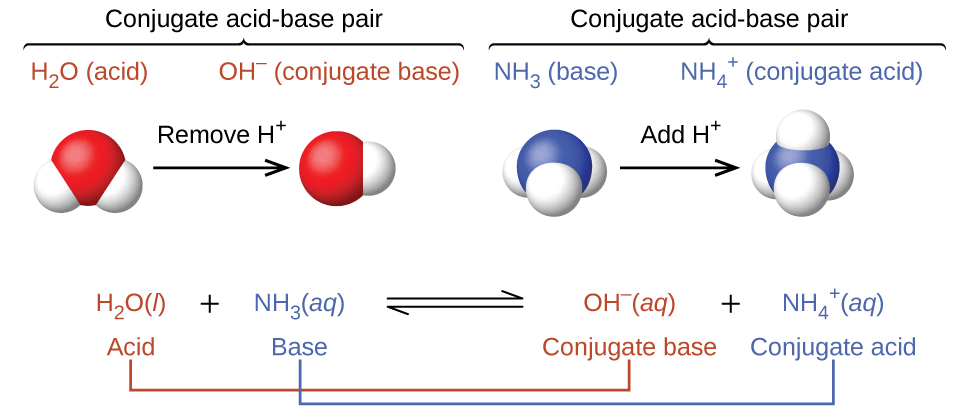 Buffers Definition Overview Expii
Buffers Definition Overview Expii
 What Is A Biological Buffer And How To Choose The Best Buffer For Your Experiment Goldbio
What Is A Biological Buffer And How To Choose The Best Buffer For Your Experiment Goldbio
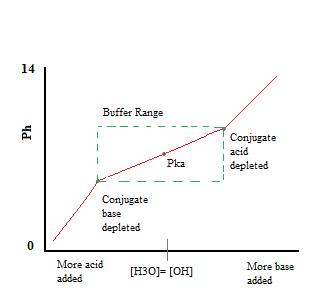 Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
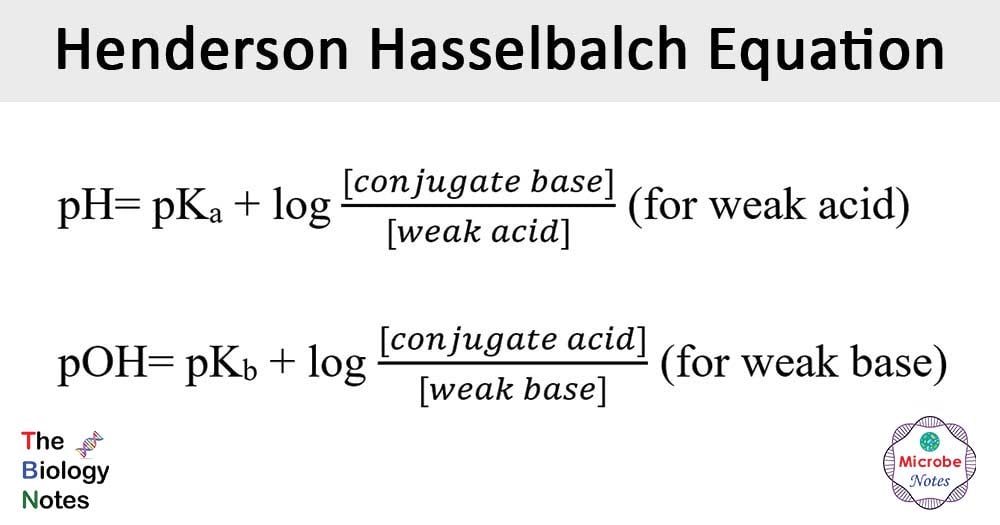 Henderson Hasselbalch Equation Microbe Notes
Henderson Hasselbalch Equation Microbe Notes
 Buffer Solutions Definition Types Preparation Examples And Videos
Buffer Solutions Definition Types Preparation Examples And Videos
 Buffers Ph Acids And Bases Biology For Non Majors I
Buffers Ph Acids And Bases Biology For Non Majors I
 Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions
Buffer Solution Preparation Of Buffer Solution Acidic Basic Buffer Buffer Action Buffer Solution Electron Configuration Solutions