What Does It Mean To Buffer Ph
Buffer systems are usually composed of a weak acid or base and its conjugate salt. A buffer system in the human body is an interaction between a weak acid-base conjugate pair that keeps the body at the proper pH.
Ph Buffers Acids And Bases Introduction To Chemistry
In basic terms the BpH is the resulting sample pH after the laboratory has added a liming material.

What does it mean to buffer ph. PH pKa. The buffer releases base ions c. Weak acids tend to be organic such as carbonic acid or acetic acid.
A buffer solution is one which resists changes in pH when small quantities of an acid or an alkali are added to it. Why does diluting buffer with water not change its pH. The logarithmic nature of the pH scale means that small changes in a soil pH can have large effects on nutrient availability and plant growth.
Shouldnt its pH approach 7 as the concentration of H becomes progressively small. The buffer releases additional hydrogen ions d. A conjugate acid-base pair is typically composed of a weak acid and the basic ion formed when that acid loses a hydrogen ion.
Buffer pH BpH This is a value that is generated in the laboratory it is not an existing feature of the soil. Buffer zone buffer noun a neutral zone between two rival powers that is created in order to diminish the danger of conflict. Known pH called a buffer to the soil-distilled water solution after the initial pH measurement is taken.
Dont confuse Alkalinity with Alkaline which means a pH of 70-140. Laboratories perform this test in order to develop lime recommendations and it actually has no other practical value. The question log shows that for a time this question quoted the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
Buffer buffer storage buffer store noun. Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications. A buffer solution more precisely pH buffer or hydrogen ion buffer is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa.
Acetic acid Sodium acetate. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. Buffers are solutions that contain a weak acid and its a conjugate base.
Buffer pH BpH This is a value that is generated in the laboratory it is not an existing feature of the soil. Buffers are aqueous solutions whose pH remains virtually unaltered by the addition of small quantities of acids or bases. The alkalinity of water is related to the pH but it is actually a different parameter.
The buffer binds the hydrogen ions to remove them from the solution. Buffer - chemistry an ionic compound that resists changes in its pH chemical science chemistry - the science of matter. Buffers are solutions that resist a change in pH on dilution or on addition of small amounts of acids or alkali.
This means that the sensor will first be rinsed off dried placed in a 7 pH neutral buffer programmed rinsed dried placed in a 4 pH acidic buffer programmed completing the calibration. A lot of biological and chemical reactions need a constant pH for the reaction to proceed. Buffers can be of following types Acidic Buffers-Mixture of weak acid and a salt of that acid with a strong alkali.
Buffers are mixtures of a salt and an acid to which when a small amount of acid or base is added the pH doesnt change. The buffer keeps the pH of a solution neutral b. Fender buffer cowcatcher pilot noun an inclined metal frame at the front of a locomotive to clear the track.
The components act in such a way that addition of an acid or base results in the formulation of a salt causing only a small change in pH. If you add an acid or a base to a buffered solution its pH will not change significantly. Buffer solutions are capable of binding hydrogen ions with the addition of acids and releasing hydrogen ions with the addition of bases.
Buffer noun chemistry an ionic compound that resists changes in its pH. It is a measure of the capacity of the water to resist changes in pH or in other words it is the buffering capacity of the water. The branch of the natural sciences dealing with the composition of substances and their properties and reactions.
What does a buffer do when hydrogen ions are added to a solution a. The amount of change in pH of the soil-distilled water solution after the addition of the buffer solution measures a given soils reserve acidity or buffering capacity. As such they can absorb excess H ions or OH ions thereby maintaining an overall steady pH in the solution.
A basic solution will have a pH above 70 while an acidic solution will have a pH below 70. As mentioned in other notes pH 4 and pH 7 buffers are the most stable and have the longest shelf life. A buffer is an aqueous solution that has a highly stable pH.
Buffers are compounds that resist changes in pH upon the addition of limited amounts of acids or bases. A buffer index can be calculated and then used to compute a lime rate needed to achieve a desired pH level. A buffering agent is a weak acid or weak base that helps maintain the pH of an aqueous solution after adding another acid or base.
Buffers are extremely useful in these systems to maintain the pH at a constant value. This does not mean that the pH of buffers does not change.
 Mcat Favorite Vhy Bicarbonate Buffer System Respiratory System Buffer Biochemistry
Mcat Favorite Vhy Bicarbonate Buffer System Respiratory System Buffer Biochemistry
 What Is Ph And What Does It Measure Chemistry Buffer Solution Paper
What Is Ph And What Does It Measure Chemistry Buffer Solution Paper
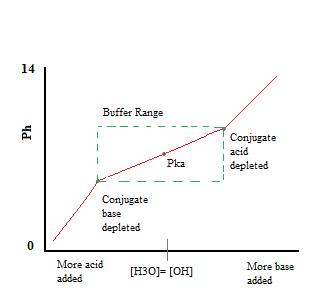 Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
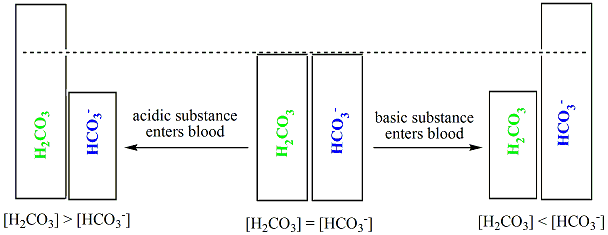 Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy
Chemistry Of Buffers And Buffers In Our Blood Article Khan Academy
 The Body S Buffer System And Ph Imbalances Helpful Youtube Video Nursing School Notes Nursing Videos Medical Laboratory Scientist
The Body S Buffer System And Ph Imbalances Helpful Youtube Video Nursing School Notes Nursing Videos Medical Laboratory Scientist
 Buffer Solutions Buffer Solution High School Chemistry Fun Learning
Buffer Solutions Buffer Solution High School Chemistry Fun Learning
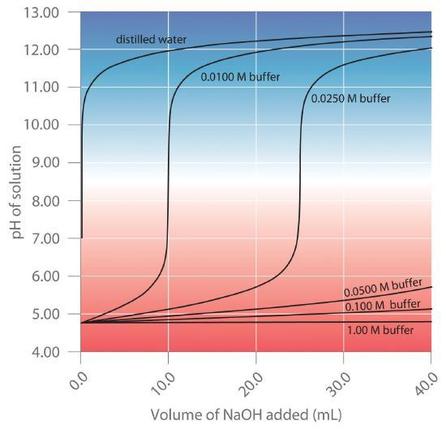 8 9 Buffer Capacity And Buffer Range Chemistry Libretexts
8 9 Buffer Capacity And Buffer Range Chemistry Libretexts
 Ph And Pka Relationship For Buffers Video Khan Academy
Ph And Pka Relationship For Buffers Video Khan Academy
 Reproducibility With Biological Buffers Sigma Aldrich
Reproducibility With Biological Buffers Sigma Aldrich






