What Is The Meaning Of Buffered Solution
Buffered buffering buffers 1. A buffer is an aqueous solution containing a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
 Buffer Solutions Study Material For Iit Jee Askiitians
Buffer Solutions Study Material For Iit Jee Askiitians
In other words a buffer is an aqueous solution of either a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.

What is the meaning of buffered solution. An example of a common buffer is a solution of acetic acid CH 3 COOH and sodium acetate. A person or thing that lessens shock or protects from damaging impact circumstances etc. Buffered solution Buffer in chemistry solution usually containing an acid and a base or a salt that tends to maintain a constant hydrogen ion concentration.
To act as a buffer for or between. A buffer may also be called a pH buffer hydrogen ion buffer or buffer solution. Definition A buffer solution is one which resists changes in pH when small quantities of an acid or an alkali are added to it.
A buffer solution more precisely pH buffer or hydrogen ion buffer is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or vice versa. The chemical known as a buffer agent resists pH changes when exposed to acids and bases when properly mixed in a solution. Buffer solution one that resists appreciable change in its hydrogen ion concentration pH when acid or alkali is added to it.
A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components. A lot of biological and chemical reactions need a constant pH for the reaction to proceed. A buffer is a regulating or buffering solution whose high concentration of acid and conjugate base allows to keep the pH of a solution stable that is when these hydrolytically active salts are.
The osmolarity and ion concentrations of the solutions match those of the human body. It is used to prevent any change in the pH of a solution regardless of solute. What is the definition of a buffer.
Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it and is thus used to prevent a solution s pH change. Buffers are extremely useful in these systems to maintain the pH at a constant value. A buffers pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it.
Ions are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained one or more electrons. A buffer is a compound that resists changes in pH when a limited amount of acid or base is added to it. A solution of a weak acid proton donor and its conjugated base proton acceptor that resists significant changes in pH upon addtion of small quantites of strong acid or base.
The buffer helps to maintain a constant pH. Now Buffer Capacity can be defined as the measure of the efficiency of a buffer in resisting its change in pH. It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable.
A buffer solution is water mixed with a chemical to give it special properties in regards to pH acidity. A buffer is an aqueous solution that consists of a mixture of a weak acid and its salt acid buffer or a weak base with its salt basic buffer. A buffer is a solution containing either a weak acid and its salt or a weak base and its salt which is resistant to changes in pH.
This is important for processes andor reactions which require specific and stable pH ranges. The chemical composition of a buffer solution usually entails a weak acid or a weak base accompanied by its conjugate salt. A buffering agent is a weak acid or weak base that helps maintain the pH of an aqueous solution after adding another acid or base.
A solution which resists the change in its pH value even on the addition of a small amount of strong acid or base is called a buffer solution or buffer. Buffer Solutions Buffers are solutions that resist a change in pH on dilution or on addition of small amounts of acids or alkali. Phosphate-buffered saline is a buffer solution commonly used in biological research.
An ionic compound usually a salt of a weak acid or base added to a solution to resist changes in its acidity or alkalinity and thus stabilize its pH. Buffer solution a solution containing such a compound. Buffer solutions are used as a means of keeping pH at a nearly constant value in a wide variety of chemical applications.
A buffer is an aqueous solution that has a highly stable pH. Its pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. If you add an acid or a base to a buffered solution its pH will not change significantly.
It is a water-based salt solution containing disodium hydrogen phosphate sodium chloride and in some formulations potassium chloride and potassium dihydrogen phosphate. Mixture of acetic acid CH 3 COOH and Sodium acetate CH 3 COONa in water.
 Buffers Definition Overview Expii
Buffers Definition Overview Expii
 Buffer Solutions Video Khan Academy
Buffer Solutions Video Khan Academy
 Buffer Solutions Water As Buffer Chemistry Lecturio Youtube
Buffer Solutions Water As Buffer Chemistry Lecturio Youtube
 A Buffered Vs A Non Buffered Solution Chem13 News Magazine University Of Waterloo
A Buffered Vs A Non Buffered Solution Chem13 News Magazine University Of Waterloo
 Ways To Get A Buffer Solution Video Khan Academy
Ways To Get A Buffer Solution Video Khan Academy
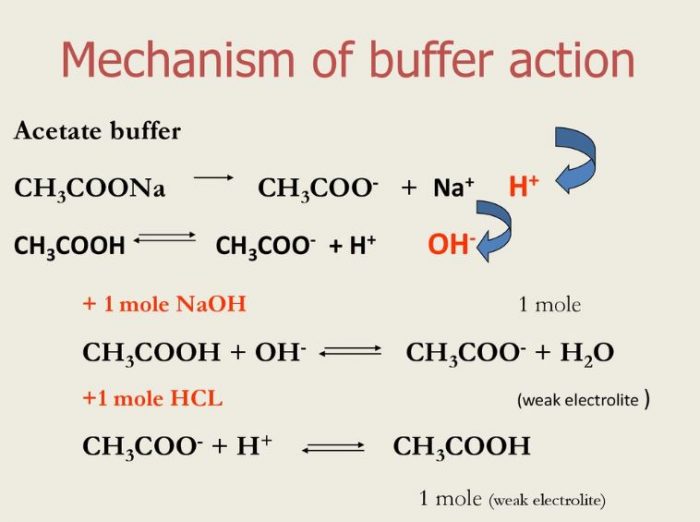 Buffer Solution And Buffer Action Chemistry Class 11 Ionic Equilibrium
Buffer Solution And Buffer Action Chemistry Class 11 Ionic Equilibrium
 Buffer Solutions Biochemistry The Biology Notes
Buffer Solutions Biochemistry The Biology Notes
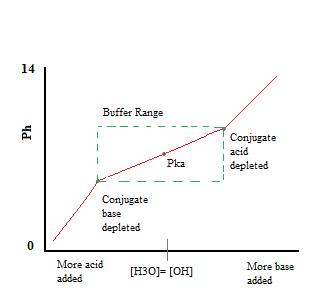 Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
Introduction To Buffers Chemistry Libretexts
Buffer Solution Solution Of Reserve Acidity Alkalinity
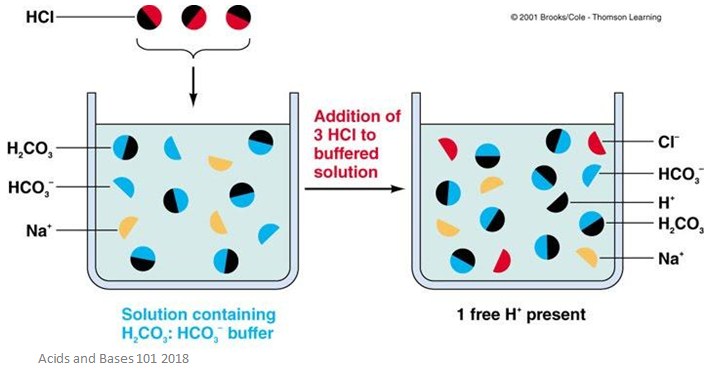 Acid Base Buffers Facts Summary Definition Chemistry Revision
Acid Base Buffers Facts Summary Definition Chemistry Revision
What Is The Role Of A Buffer In A Pharmacy Quora
 What Is A Buffer Solution And How Does It Work In Hindi And Urdu Youtube
What Is A Buffer Solution And How Does It Work In Hindi And Urdu Youtube
 Buffer Solutions Definition Types Preparation Examples And Videos
Buffer Solutions Definition Types Preparation Examples And Videos


